24 Jan Eye of Horus
The ancients believed that the eyes have the power to cast spells with a single glance. They also believed that the effects of the evil eye can be defeated by the “good eye”. These beliefs paved the way for the myths about Horus to be embraced by ancient Egyptians.
The Eye of Horus became the most popular ancient Egyptian eye symbol associated with good health, protection, and royal power. In ancient Egypt, the Eye of Horus was just as popular and used as frequently as the Eye of Ra. Both Egyptian Eye symbols stand for the powerful “all-seeing-eye” in ancient Egyptian beliefs and are often used interchangeably, but are actually two distinct symbols that are based on two different legends for two different gods. While the Eye of Ra belonged to the sun god Ra and was based on a legend of fury, hate, violence and destruction, the Eye of Horus wes based on a legend of healing and regeneration.
The Stories Behind the Symbol
Both legends of the Egyptian gods Horus and Ra have varying versions, with many details rendered unclear as a result. Horus was a mighty god associated with the heavens. He was the son of the Egyptian Lord of the Underworld, Osiris and his sister-wife Isis, the goddess of life and magic. In the most widely accepted version of the legend behind the Horus symbol, it is said that Osiris was killed and mutilated by Seth, his own brother, himself the god of fire, chaos, trickery, deserts, storms, disorder, envy, violence and foreigners. Isis thereafter gathered Osiris’ body parts and resurrected him just long enough for her to conceive his heir, Horus. Afterward, Osiris went on to become the god of the underworld.
Isis raised Horus on her own. When Horus came of age, he sought revenge against Seth and fought a series of legendary battles as to who would inherit the throne to the netherworld. It was in one of these battles that Seth lost his testicles and Horus lost his right eye when Seth tore it up into six pieces. Other versions of the legend say it was the left eye. Horus eventually won. The Egyptian god of the moon and also the wisest of the Egyptian gods Thoth restored Horus’ eye. In some versions, it was Horus’ known consort and goddess of joy and motherhood Hathor who restored his eye. This newly restored eye was then named Wadjet (or wedjat, udjat), meaning “healthy” or “whole”.
Different Meanings and Uses of the Eye of Horus in Ancient Egypt
The ancient Egyptians believed that Horus’ restored eye had healing powers. Then began the practice of making amulets of the Eye of Horus using various materials like gold, carnelian and lapis lazuli.
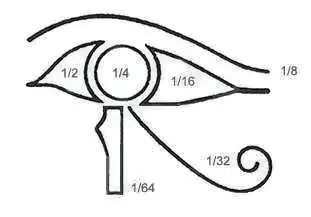
The symbol itself has six parts, each representing the six broken pieces of the damaged eye. Each part was assigned a fraction as a unit of measurement. In the ancient Egyptian measurement system, the Eye of Horus represented how parts of a whole are measured. Interestingly, they add up to 63/64, which itself symbolizes the fact that nothing is perfect.
Each of the six parts is also assigned to different senses. The eyebrow (1/8) represents thought. The pupil (1/4) represents sight. The left side (1/16) represents hearing and the right side (1/2) represents the sense of smell. The curved tail (1/32) represents the sense of taste and the stalk (1/64) represents touch.
How is the Eye of Horus Used Today?